- RiuNet repositorio UPV
- :
- Investigación
- :
- Tesis doctorales
- :
- Ver ítem
JavaScript is disabled for your browser. Some features of this site may not work without it.
Buscar en RiuNet
Listar
Mi cuenta
Estadísticas
Ayuda RiuNet
Admin. UPV
Bases estructurales de la señalización y regulación por nitrógeno y procesos asociados
Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
Ficheros en el ítem
| dc.contributor.advisor | Rubio Zamora, Vicente
|
es_ES |
| dc.contributor.author | Tremiño Agulló, Lorena
|
es_ES |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2019-03-12T07:30:51Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2019-03-12T07:30:51Z | |
| dc.date.created | 2019-01-28 | |
| dc.date.issued | 2020-01-28 | es_ES |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10251/117999 | |
| dc.description | Tesis por compendio | es_ES |
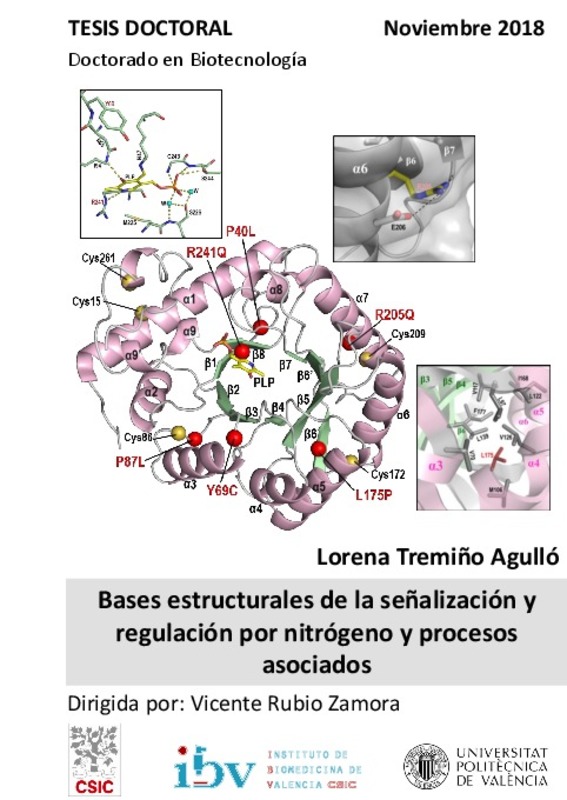
| dc.description.abstract | [ES] Enmarcada en la línea de investigación de nuestro laboratorio sobre señalización por nitrógeno principalmente en la cianobacteria Synechococcus elongatus PCC7942, con esfuerzos centrados en las proteínas PII y PipX y su red de señalización, esta Tesis amplía el espectro de moléculas investigadas en relación con dicha red. Estudia y caracteriza el miembro no canónico de la superfamilia de la proteína PII denominado CutA, generalmente anotado como de protección frente a metales divalentes, altamente conservado en todos los dominios de la vida (incluidos animales y el ser humano). En ella examinamos la posible protección frente a metales provista por CutA en dos bacterias muy distantes, Escherichia coli y Synechococcus elongatus, usando knockouts para ambas del gen que codifica para CutA. Ni los estudios de complementación en E. coli del gen silvestre ni los observacionales de sensibilidad a metales en S. elongatus han dado soporte a la función anotada para CutA, a pesar de que demostramos mediante seguimiento turbidimétrico que el Cu2+ hace agregar a la proteína CutA pura de S. elongatus (producida recombinantemente) y por tanto se une a ella, aunque con una afinidad baja por comparación con las concentraciones tóxicas de este metal para dicha cianobacteria. Buscando profundizar en el conocimiento de CutA, hemos determinado a muy alta resolución mediante difracción de rayos X la estructura de esta proteína de S. elongatus, sin evidenciar complejo alguno con cobre, pero demostrando que los tres bolsillos intersubunidades en el homotrímero de CutA son capaces de transportar moléculas orgánicas (en nuestro caso Bis-Tris). Estos resultados apoyan una posible función de CutA basada en la unión a estos bolsillos de biomoléculas neutras o positivamente cargadas y capaces de formar varios puentes de hidrógeno con las paredes de potencial negativo y fuerte carácter polar de estos bolsillos. También hemos estudiado la proteína PipY de S. elongatus, identificada recientemente como pareja funcional de la antes mencionada PipX, determinando sus propiedades espectroscópicas, unión de piridoxal fosfato (PLP) y resolviendo su estructura mediante difracción de rayos X. Probamos que PipY es monomérica y que tiene PLP unido. Su estructura no apoya que sea un enzima, siendo aparentemente apropiada para ejercer una posible función en la homeostasis de PLP. Dado que muy recientemente se ha descrito una epilepsia genética humana dependiente de vitamina B6 debida a mutaciones en el gen humano ortólogo de pipY, PROSC (ahora llamado PLPBP; codifica la proteína PLPHP), usamos inicialmente PipY de S. elongatus y luego PROSC humana como banco de pruebas de la patogenicidad de las mutaciones que se han asociado a esta epilepsia, utilizando para ello mutagénesis dirigida y producción de las formas silvestre y mutantes de estas proteínas, comparando sus propiedades. Estos estudios han demostrado la patogenicidad y establecido mecanismos para la misma para cada una de las mutaciones de cambio de sentido de PROSC descritas hasta ahora en esta epilepsia. Nuestros estudios han representado un importante avance en la comprensión de las proteínas de tipo PipY y de la epilepsia asociada a la forma humana de las mismas. | es_ES |
| dc.description.abstract | [CA] Emmarcada en la línia d'investigació del nostre laboratori de senyalització per nitrogen principalment en el cianobacteri Synechococcus elongatus PCC7942, amb esforços centrats en les proteïnes PII i PipX i la seua xarxa de senyalització, esta Tesi amplia l'espectre de molècules investigades en relació amb la dita xarxa. Estudia i caracteritza el membre no canònic de la superfamília de la proteïna PII denominat CutA, generalment anotat com de protecció a metalls divalents, altament conservat en tots els dominis de la vida (inclosos animals i l'ésser humà). En ella examinem la possible protecció front a metalls proveïda per CutaA en dos bacteris molt distants, Escherichia coli i Synechococcus elongatus, usant knockouts del gen que codifica CutA per a ambdues. Ni els estudis de complementació en E. coli del gen silvestre ni els observacionals de sensibilitat a metalls en S. elongatus han donat suport a la funció anotada per CutA, tot i que vam demostrar mitjançant seguiment turbidimétric que el Cu2 + fa agregar a la proteïna CutA pura de S. elongatus (produïda de forma recombinant) i per tant s'uneix a ella, encara que amb una afinitat baixa per comparació amb les concentracions tòxiques d'aquest metall per a aquest cianobacteri. Buscant aprofundir en el coneixement de CutA, hem determinat a molt alta resolució mitjançant difracció de raigs X l'estructura d'aquesta proteïna de S. elongatus, sense evidenciar cap complex amb coure, però demostrant que les tres cavitats formades entre les subunitats del homotrimer de CutA són capaços de transportar molècules orgàniques (en el nostre cas Bis-Tris). Aquests resultats donen suport a una possible funció de CutA basada en la unió a aquestes cavitats de biomolècules neutres o positivament carregades i capaços de formar diversos ponts d'hidrogen amb les parets de potencial negatiu i fort caràcter polar d'aquestes cavitats. També hem estudiat la proteïna PipY de S. elongatus, identificada recentment com a parella funcional de l'abans esmentada PipX, determinant les seves propietats espectroscòpiques, unió de piridoxal fosfat (PLP) i resolent la seva estructura mitjançant difracció de raigs X. Vam provar que PipY és monomèrica i que té PLP unit. La seva estructura no recolza que sigui un enzim, sent aparentment apropiada per a exercir una possible funció en l'homeòstasi de PLP. Atès que molt recentment s'ha descrit una epilèpsia genètica humana dependent de vitamina B6 deguda a mutacions en el gen humà ortòleg de pipY, PROSC (ara anomenat PLPBP; codifica la proteïna PLPHP), fem servir inicialment PipY de S. elongatus i després PROSC humana com banc de proves de la patogenicitat de les mutacions que s'han associat a aquesta epilèpsia, utilitzant mutagènesi dirigida i produint les formes silvestre i mutants d'aquestes proteïnes, comparant les seves propietats. Aquests estudis han demostrat la patogenicitat i establert mecanismes per a la mateixa per a cadascuna de les mutacions de canvi de sentit de PROSC descrites fins ara en aquesta epilèpsia. Els nostres estudis han representat un important avanç en la comprensió de les proteïnes de tipus PipY i de l'epilèpsia associada a la forma humana de les mateixes. | es_ES |
| dc.description.abstract | [EN] In the context of research of our laboratory on nitrogen signaling mainly in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus PCC7942, with efforts focused on the PII and PipX proteins and their signaling network, this Thesis extends the spectrum of molecules investigated in relation to such network. It studies and characterizes the non-canonical member of the PII protein superfamily named CutA, a highly conserved protein in all domains of life (including animals and humans) which is generally annotated as protecting against divalent metals. We examine the possible protection provided by CutA against metals, using knockouts for the CutA-encoding gene of two phylogenetically distant bacteria, Escherichia coli and Synechococcus elongatus PCC7942. Neither complementation studies in E. coli by the wild-type gene, nor observational studies of sensitivity to metals in the S. elongatus knockout have supported the function annotated for CutA, although we show by turbidimetric monitoring that Cu2+ causes aggregation of pure S. elongatus CutA (produced recombinantly) and therefore binds to it, although with a low affinity by comparison with the concentrations of this metal that are toxic for this cyanobacterium. Aiming at getting further insight into CutA, we have determined at very high resolution, by X-ray diffraction, the structure of this protein of S. elongatus, failing to observe Cu2+ bound in this structure, but showing that the three pockets formed at intersubunit boundaries in the CutA homotrimer are capable of transporting organic molecules (in our case Bis-Tris) without inducing conformational changes in the protein. This finding supports a possible function of CutA based on the binding to these pockets of neutral or positively charged biomolecules capable of forming several hydrogen bonds with the pocket walls, which are endowed with negative potential and have a strong polar character. We have also studied the PipY protein of S. elongatus, recently identified as a functional partner of the aforementioned PipX, determining its spectroscopic properties, binding of pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) and solving its structure by X-ray diffraction. We prove that PipY is monomeric and has PLP attached. Its structure does not favor an enzymatic role of PipY, being more appropriate for exerting a possible function in the homeostasis of PLP. Given the very recent description of a human vitamin B6-dependent genetic epilepsy associated to mutations in the human orthologue of the pipY gene, PROSC (now called PLPBP, encoding the PROSC protein, now named PLPHP), we used first S. elongatus PipY and afterwards and more extensively human PROSC to test by site-directed mutagenesis the pathogenicity of the mutations that have been associated with this epilepsy. These studies have demonstrated the pathogenicity and established mechanisms for this pathogenicity for each of the missense mutations reported thus far in patients with PROSC-associated epilepsy. Our studies represent an important advance in the understanding of PipY-like proteins and of epilepsy associated with the human form thereof. | es_ES |
| dc.description.sponsorship | Para la realización de esta Tesis, Lorena Tremiño Agulló ha disfrutado de una Beca de Formación de Personal Investigador (FPI) (BES-2012-058304) otorgado por el Ministerio de Economía, Industria y Competitividad. El trabajo se ha llevado a cabo en el grupo 739 del CIBERER-Instituto de Salud Carlos III (IP, V. Rubio) y se ha enmarcado dentro de los proyectos: -“Luz estructural sobre señalización y regulación por nitrógeno y sobre biosíntesis de arginina/urea, sus errores congénitos, y su conexión con biología del envejecimiento”, (BFU2011-30407) del Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad del Gobierno de España (Investigador principal,V. Rubio). -“Una mirada molecular al control de la detoxificación de amonio y a sus patologías y errores congénitos, y a la señalización por amonio. En busca del papel de la proteína CutA”, (BFU2014-58229) del Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad del Gobierno de España (Investigador principal, V. Rubio). -"BioMeder. Genes, proteínas y rutas de señalización en enfermedades raras" (PrometeoII/2014/029) de la Conselleria d'Educació de la Generalitat Valenciana (investigadores, P. Sanz, A. Marina y V. Rubio). | es_ES |
| dc.language | Español | es_ES |
| dc.publisher | Universitat Politècnica de València | es_ES |
| dc.rights | Reserva de todos los derechos | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Estructura de proteínas | es_ES |
| dc.subject | COG0325 | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Superfamilia PII | es_ES |
| dc.subject | CutA | es_ES |
| dc.subject | PLPBP | es_ES |
| dc.subject | PLPHP | es_ES |
| dc.subject | PROSC | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Piridoxal fosfato (PLP) | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Epilepsia dependiente de vitamina B6 | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Mutaciones hereditarias | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Cobre | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Termoestabilidad | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Correlación estructura-función | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Proteínas recombinantes | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Mutagénesis dirigida | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Synechococcus elongatus PCC7942 | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Cristalografía, Difracción de rayos X. | es_ES |
| dc.subject.classification | BIOQUIMICA Y BIOLOGIA MOLECULAR | es_ES |
| dc.title | Bases estructurales de la señalización y regulación por nitrógeno y procesos asociados | es_ES |
| dc.type | Tesis doctoral | es_ES |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.4995/Thesis/10251/117999 | es_ES |
| dc.relation.projectID | info:eu-repo/grantAgreement/MINECO//BES-2012-058304/ES/BES-2012-058304/ | es_ES |
| dc.relation.projectID | info:eu-repo/grantAgreement/MICINN//BFU2011-30407/ES/LUZ ESTRUCTURAL SOBRE SEÑALIZACION Y REGULACION POR NITROGENO Y SOBRE BIOSINTESIS DE ARGININA%2FUREA, SUS ERRORES CONGENITOS, Y SU CONEXION CON BIOLOGIA DEL ENVEJECIMIENTO/ | es_ES |
| dc.relation.projectID | info:eu-repo/grantAgreement/MINECO//BFU2014-58229-P/ES/UNA MIRADA MOLECULAR AL CONTROL DE LA DETOXIFICACION DE AMONIO Y A SUS PATOLOGIAS Y ERRORES CONGENITOS, A LA SEÑALIZACION POR NITROGENO. EN BUSCA DEL PAPEL DE LA PROTEINA CUTA/ | es_ES |
| dc.relation.projectID | info:eu-repo/grantAgreement/GVA//PROMETEOII%2F2014%2F029/ES/Genes, proteínas y rutas de señalización en enfermedades raras/ | es_ES |
| dc.rights.accessRights | Abierto | es_ES |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Universitat Politècnica de València. Departamento de Biotecnología - Departament de Biotecnologia | es_ES |
| dc.description.bibliographicCitation | Tremiño Agulló, L. (2019). Bases estructurales de la señalización y regulación por nitrógeno y procesos asociados [Tesis doctoral]. Universitat Politècnica de València. https://doi.org/10.4995/Thesis/10251/117999 | es_ES |
| dc.description.accrualMethod | TESIS | es_ES |
| dc.type.version | info:eu-repo/semantics/acceptedVersion | es_ES |
| dc.relation.pasarela | TESIS\10160 | es_ES |
| dc.contributor.funder | Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad | es_ES |
| dc.contributor.funder | Generalitat Valenciana | es_ES |
| dc.contributor.funder | Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación | es_ES |
| dc.description.compendio | Compendio | es_ES |
Este ítem aparece en la(s) siguiente(s) colección(ones)
-
Tesis doctorales [5389]