JavaScript is disabled for your browser. Some features of this site may not work without it.
Buscar en RiuNet
Listar
Mi cuenta
Estadísticas
Ayuda RiuNet
Admin. UPV
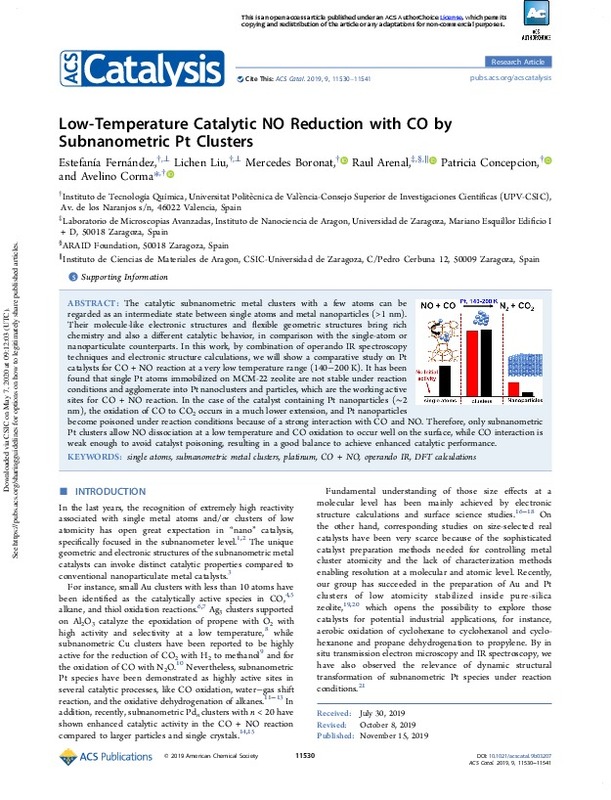
Low-Temperature Catalytic NO Reduction with CO by Subnanometric Pt Clusters
Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
Ficheros en el ítem
| dc.contributor.author | Fernández-Villanueva, Estefanía
|
es_ES |
| dc.contributor.author | Liu, Lichen
|
es_ES |
| dc.contributor.author | Boronat Zaragoza, Mercedes
|
es_ES |
| dc.contributor.author | Arenal, Raul
|
es_ES |
| dc.contributor.author | Concepción Heydorn, Patricia
|
es_ES |
| dc.contributor.author | Corma Canós, Avelino
|
es_ES |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2020-09-24T12:29:35Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2020-09-24T12:29:35Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2019-12-06 | es_ES |
| dc.identifier.issn | 2155-5435 | es_ES |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10251/150654 | |
| dc.description.abstract | [EN] The catalytic subnanometric metal clusters with a few atoms can be regarded as an intermediate state between single atoms and metal nanoparticles (>1 nm). Their molecule-like electronic structures and flexible geometric structures bring rich chemistry and also a different catalytic behavior, in comparison with the single-atom or nanoparticulate counterparts. In this work, by combination of operando IR spectroscopy techniques and electronic structure calculations, we will show a comparative study on Pt catalysts for CO + NO reaction at a very low temperature range (140-200 K). It has been found that single Pt atoms immobilized on MCM-22 zeolite are not stable under reaction conditions and agglomerate into Pt nanoclusters and particles, which are the working active sites for CO + NO reaction. In the case of the catalyst containing Pt nanoparticles (similar to 2 nm), the oxidation of CO to CO2 occurs in a much lower extension, and Pt nanoparticles become poisoned under reaction conditions because of a strong interaction with CO and NO. Therefore, only subnanometric Pt clusters allow NO dissociation at a low temperature and CO oxidation to occur well on the surface, while CO interaction is weak enough to avoid catalyst poisoning, resulting in a good balance to achieve enhanced catalytic performance. | es_ES |
| dc.description.sponsorship | This work has been supported by the European Union through the European Research Council (grant ERC-AdG-2014671093, SynCatMatch) and the Spanish government through the "Severo Ochoa Program" (SEV-2016-0683) and MAT2017-82288-C2-1-P projects. L.L. thanks ITQ for providing a contract. E.F. thanks MINECO for her fellowship SVP-2013-068146. The authors also thank Microscopy Service of UPV for the TEM and STEM measurements. The HRSTEM studies were conducted at the Laboratorio de Microscopias Avanzadas, Universidad de Zaragoza, Spain. RA. acknowledges support from Spanish MINECO grant MAT2016-79776-P (AEI/FEDER, UE), from the Government of Aragon and the European Social Fund (grant number E13_17R, FEDER, UE), and from the European Union H2020 program "ESTEEM3" (grant number 823717). Red Espanola de Supercomputacion (RES) and Centre de Calcul de la Universitat de Valencia are acknowledged for computational resources and technical support. | es_ES |
| dc.language | Inglés | es_ES |
| dc.publisher | American Chemical Society | es_ES |
| dc.relation.ispartof | ACS Catalysis | es_ES |
| dc.rights | Reconocimiento - No comercial (by-nc) | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Single atoms | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Subnanometric metal clusters | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Platinum | es_ES |
| dc.subject | CO plus NO | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Operando IR | es_ES |
| dc.subject | DFT calculations | es_ES |
| dc.subject.classification | QUIMICA ORGANICA | es_ES |
| dc.title | Low-Temperature Catalytic NO Reduction with CO by Subnanometric Pt Clusters | es_ES |
| dc.type | Artículo | es_ES |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.1021/acscatal.9b03207 | es_ES |
| dc.relation.projectID | info:eu-repo/grantAgreement/EC/H2020/671093/EU/MATching zeolite SYNthesis with CATalytic activity/ | es_ES |
| dc.relation.projectID | info:eu-repo/grantAgreement/MINECO//SVP-2013-068146/ES/SVP-2013-068146/ | es_ES |
| dc.relation.projectID | info:eu-repo/grantAgreement/EC/H2020/823717/EU/Enabling Science and Technology through European Electron Microscopy/ | es_ES |
| dc.relation.projectID | info:eu-repo/grantAgreement/AEI/Plan Estatal de Investigación Científica y Técnica y de Innovación 2013-2016/MAT2017-82288-C2-1-P/ES/MATERIALES HIBRIDOS MULTIFUNCIONALES BASADOS EN NANO-UNIDADES ESTRUCTURALES ACTIVAS/ | es_ES |
| dc.relation.projectID | info:eu-repo/grantAgreement/MINECO//MAT2016-79776-P/ES/AJUSTE DE LAS PROPIEDADES OPTOELECTRONICAS DE NANOESTRUCTURAS: SU (TRANS)FORMACION Y ESTUDIOS AVANVAZADOS SOBRE SU CONFIGURACION ATOMICA Y ESTUCTURAL/ | es_ES |
| dc.relation.projectID | info:eu-repo/grantAgreement/Gobierno de Aragón//E13_17R/ | es_ES |
| dc.relation.projectID | info:eu-repo/grantAgreement/MINECO//SEV-2016-0683/ | es_ES |
| dc.rights.accessRights | Abierto | es_ES |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Universitat Politècnica de València. Instituto Universitario Mixto de Tecnología Química - Institut Universitari Mixt de Tecnologia Química | es_ES |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Universitat Politècnica de València. Departamento de Química - Departament de Química | es_ES |
| dc.description.bibliographicCitation | Fernández-Villanueva, E.; Liu, L.; Boronat Zaragoza, M.; Arenal, R.; Concepción Heydorn, P.; Corma Canós, A. (2019). Low-Temperature Catalytic NO Reduction with CO by Subnanometric Pt Clusters. ACS Catalysis. 9(12):11530-11541. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.9b03207 | es_ES |
| dc.description.accrualMethod | S | es_ES |
| dc.relation.publisherversion | https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.9b03207 | es_ES |
| dc.description.upvformatpinicio | 11530 | es_ES |
| dc.description.upvformatpfin | 11541 | es_ES |
| dc.type.version | info:eu-repo/semantics/publishedVersion | es_ES |
| dc.description.volume | 9 | es_ES |
| dc.description.issue | 12 | es_ES |
| dc.identifier.pmid | 31840009 | es_ES |
| dc.identifier.pmcid | PMC6902616 | es_ES |
| dc.relation.pasarela | S\410515 | es_ES |
| dc.contributor.funder | Gobierno de Aragón | es_ES |
| dc.contributor.funder | European Regional Development Fund | es_ES |
| dc.contributor.funder | Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad | es_ES |
| dc.contributor.funder | Agencia Estatal de Investigación | es_ES |