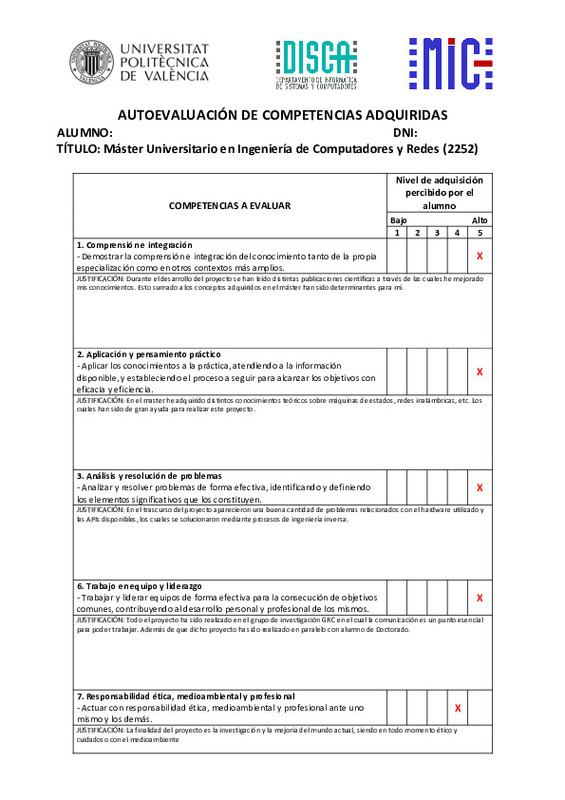
|
Resumen:
|
El presente proyecto nace de la necesidad de crear un algoritmo para el control de enjambres de multicópteros para múltiples tareas. Para ello, dicho algoritmo debe ser compatible con el protocolo de comunicación MAVLink ...[+]
El presente proyecto nace de la necesidad de crear un algoritmo para el control de enjambres de multicópteros para múltiples tareas. Para ello, dicho algoritmo debe ser compatible con el protocolo de comunicación MAVLink por ser el más extendido entre las controladoras de vuelo abiertas. Las comunicaciones a nivel de transporte entre las aeronaves se realizan mediante el protocolo UDP, asegurando así una latencia mínima y altas tasas de transferencia. El nivel de acceso al medio (MAC) y la capa física (PHY) se controlan mediante el estándar IEEE 802.11a en modo ad-hoc bajo la banda de los 5,8GHz para asegurar el ancho de banda necesario, y mitigar las interferencias entre el algoritmo y los sistemas de control externos de las aeronaves. El algoritmo se ejecuta desde una Raspberry Pi siguiendo una máquina de estados que, a su vez, se comunica mediante una conexión en serie con la controladora de vuelo. Ésta es la encargada final de comunicar las órdenes en formato MAVLink a una controladora de vuelo PIXHAWK. Para el desarrollo y la verificación del algoritmo se utiliza el simulador de vuelo Ardusim, que, mediante la replicación de múltiples instancias del simulador de aeronaves SITL, permite la simulación de hasta 256 aeronaves en un mismo sistema.
[-]
The present project is born as a requirement to create an algorithm for the control of an UAV swarm applicable to multiple tasks. For this reason, this algorithm must be compatible with the MAVLink communications protocol, ...[+]
The present project is born as a requirement to create an algorithm for the control of an UAV swarm applicable to multiple tasks. For this reason, this algorithm must be compatible with the MAVLink communications protocol, as it is the most widespread among open-source flight controllers. Communications at the transport layer between aircrafts are made using the UDP protocol, thus ensuring a minimum latency and high transfer rates. The media access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) are controlled by the IEEE 802.11a standard in ad-hoc mode under the 5.8GHz band to ensure the necessary bandwidth and mitigate the interference between the algorithm and the external control systems of the aircraft. The algorithm is executed from a Raspberry Pi following a state machine which communicates through a serial connection with the flight controller. This is the final responsible for communicating orders in MAVLink format to a PIXHAWK flight controller. Ardusim is used for the development and verification of the algorithm, which through the replication of multiple instances of the SITL aircraft simulator, allows the simulation of up to 256 aircrafts in the same system.
[-]
|