|
Resumen:
|
[ES] Recientemente, varios hallazgos han destacado el papel crucial del viroma humano en la salud y enfermedad del huésped, así como su potencial como marcador de diagnóstico e incluso terapia. A medida que este campo se ...[+]
[ES] Recientemente, varios hallazgos han destacado el papel crucial del viroma humano en la salud y enfermedad del huésped, así como su potencial como marcador de diagnóstico e incluso terapia. A medida que este campo se ha ido expandiendo, han surgido varias limitaciones. Una de las restricciones más importantes está relacionada con el protocolo de extracción de ácidos nucleicos virales. Diversos experimentos han señalado que el método de extracción influye en gran medida en los resultados, determinando la cantidad y calidad del ARN y ADN analizados. Por tanto, es necesario encontrar un método de extracción de viroma humano preciso, que garantice resultados reproducibles y fiables. Siguiendo esta línea de pensamiento, en este trabajo fin de grado se han propuesto y probado tres protocolos de extracción alternativos en muestras fecales de varios voluntarios diagnosticados genéticamente con el síndrome de Lynch, una condición hereditaria que aumenta el riesgo de ciertos tipos de cáncer, como el cáncer colorrectal. Siendo dos de ellos altamente específicos para virus, implicando un enriquecimiento de `virus-like particles¿ en la muestra previo a la extracción de ARN y ADN. El otro método siendo más general, permitiendo la extracción de la población total microbiana, incluyendo virus. El objetivo de este trabajo es evaluar cuál de estos métodos de extracción optimiza los resultados de secuenciación, en términos de rendimiento de lecturas virales, para poder seleccionar la alternativa más eficiente para su posterior implementación en la línea de investigación del laboratorio.
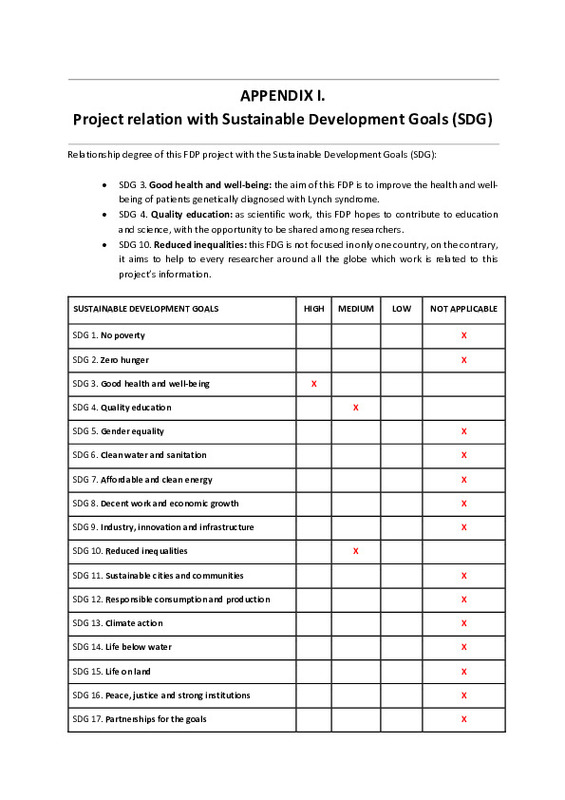
Este proyecto se relaciona con los siguientes Objetivos de Desarrollo Sostible (ODS): Salud y bienestar (ODS 3), Educación de calidad (ODS 4) y Reducción de las desigualdades (ODS 10).
[-]
[EN] Recently, several findings have highlighted the crucial role of human virome in health and host¿s disease, as well as its potential as future diagnosis marker or even therapy. As this field has expanded, limitations ...[+]
[EN] Recently, several findings have highlighted the crucial role of human virome in health and host¿s disease, as well as its potential as future diagnosis marker or even therapy. As this field has expanded, limitations have been appearing. One of the most important is related to viral nucleic acids extraction protocol as diverse experiments have pointed out that the extraction method is highly influencing the results, determining the quantity and quality of the RNA and DNA analyzed. Then, it is demanding to find an accurate extraction method for human virome that ensures reproducible and faithful results. Following this idea, three alternative extraction protocols have been tested on fecal samples from several volunteers genetically diagnosed with Lynch syndrome, a hereditary condition that increases the risk of certain cancers, such as colorectal cancer. Two of them being highly specific for viruses, involving an enrichment of virus¿like particles in the sample prior to RNA and DNA extraction. The other one being a bulk method enabling the extraction of the whole microbiome including viruses. The aim of this work is to assess which of these extraction methods optimizes the sequencing results in terms of viral reads yield to be able to select the most efficient one for its implementation in the laboratory research line.
This project is related to the following Sustainable Development Goals (SDG): Good health and well-being (SDG 3), Quality education (SDG 4) and Reduced inequalities (SDG 10).
[-]
|