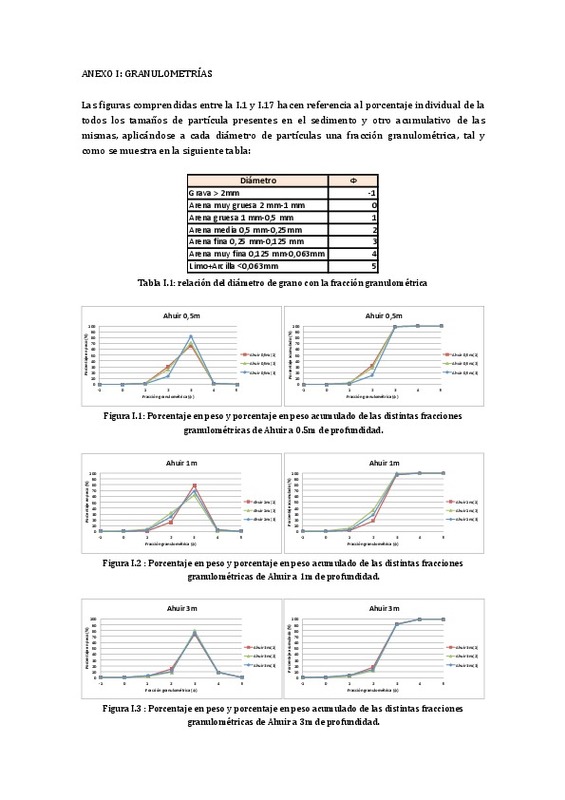
|
Resumen:
|
Las diferentes características físicas, químicas y biológicas que presentan las playas arenosas, van a estar condicionando la distribución y abundancia de la macrofauna bentónica. Se considera que la influencia de factores ...[+]
Las diferentes características físicas, químicas y biológicas que presentan las playas arenosas, van a estar condicionando la distribución y abundancia de la macrofauna bentónica. Se considera que la influencia de factores físicos son los más influyentes, siendo consideradas las interacciones biológicas de menor importancia en algunas ocasiones, debido a que el alto dinamismo de estas playas depende en mayor medida de las características físicas. Pero cabe destacar que la estructura de las comunidades depende de la interacción de factores tanto bióticos como abióticos, pasando a ser la caracterización físico-biológica la más adecuada para explicar la regulación y dinámica en los ecosistemas marinos. Se replanteó el estudio de tres playas (playa norte de Gandia-Ahuir, Venecia y Marenys de Rafalcaid) del sector sur del Golfo de Valencia con distintas características morfológicas, hidrodinámicas y fisicoquímicas del sedimento y agua, muestreándose a distintas profundidades, entre 0.5 y 5 m. de profundidad, con tal de establecer la distribución y abundancia de sus especies, así como la similitud entre las comunidades de cada una de ellas, y los parámetros más influyentes en la distribución y abundancia de la macrofauna.
Tanto la abundancia de especies como la frecuencia y la riqueza difirieron entre las tres playas, aunque se observó un claro patrón batimétrico. A medida que aumentaba la profundidad se observó mayor homogeneidad debido a que la influencia de la hidrodinámica diferencial en cada playa es menor. La mayor riqueza se presentó en Venecia debido a su menor exposición y por tanto menor influencia de las variables físicas. En cuanto a las variables más influyentes en la estructura de las comunidades, fueron la profundidad, la presencia de limos y arcillas y la concentración de nutrientes.
[-]
Distribution and abundance of benthic macrofauna in sandy beaches can be influenced by different physical, chemical and biological parameters. It is considered that physical factors are the most important and biological ...[+]
Distribution and abundance of benthic macrofauna in sandy beaches can be influenced by different physical, chemical and biological parameters. It is considered that physical factors are the most important and biological interactions are negligible, due to the high dynamism of these beaches depends on highly the physical characteristics. But structure of communities depends on interaction of biotic and abiotic factors, becoming physical-biological characterization the most suitable to explain regulation and dynamics in marine ecosystems. This study comprised three beaches (north beach of Gandia-Ahuir, Venecia and Marenys Rafalcaid) in the southern Gulf of Valencia. These beaches have different morphology, hydrodynamism and physicochemical characteristics of sediment and water. They were sampled at different depths between 0.5 and 5m depth, to establish distribution and abundance of species, and similarity between the communities of each one, and to determine the most influential parameters in the distribution and abundance of macrofauna.
Species abundance, frequency and richness differed between the three beaches, showing a bathymetric pattern. The deeper the beach is the higher homogeneity in the communities it was observed, because of the influence of differential hydrodynamism was small. Venecia presented more richness than the other beaches due to it presents the lowest exposure and therefore a minor influence of physical variables. Finally, the most influential variables in the structure of communities were depth, presence of silt and clay and nutrient concentration.
[-]
|