JavaScript is disabled for your browser. Some features of this site may not work without it.
Buscar en RiuNet
Listar
Mi cuenta
Estadísticas
Ayuda RiuNet
Admin. UPV
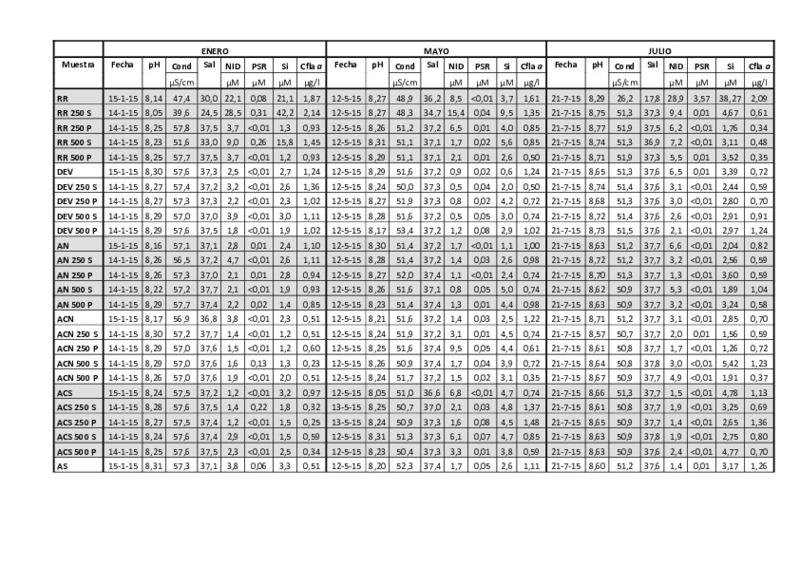
Calidad de las aguas costeras del municipio de Denia
Mostrar el registro completo del ítem
Alventosa Ferri, J. (2015). Calidad de las aguas costeras del municipio de Denia. Universitat Politècnica de València. http://hdl.handle.net/10251/55161
Por favor, use este identificador para citar o enlazar este ítem: http://hdl.handle.net/10251/55161
Ficheros en el ítem
Metadatos del ítem
| Título: | Calidad de las aguas costeras del municipio de Denia | |||
| Autor: | Alventosa Ferri, Jordi | |||
| Director(es): | Bordehore Fontanet, Cesar | |||
| Entidad UPV: |
|
|||
| Fecha acto/lectura: |
|
|||
| Resumen: |
La calidad de las aguas costeras en muchas regiones del mundo se ha deteriorado en los
últimos años a medida que la población humana y las actividades se han incrementado en las
regiones costeras, y en especial en la ...[+]
The quality of coastal waters in many regions of the world has deteriorated in recent years as
the human population and activities have increased in the coastal regions, especially on the
Mediterranean coast. Human ...[+]
|
|||
| Palabras clave: |
|
|||
| Derechos de uso: | Reserva de todos los derechos | |||
| Editorial: |
|
|||
| Titulación: |
|
|||
| Tipo: |
|
recommendations
Este ítem aparece en la(s) siguiente(s) colección(ones)
-
EPSG - Trabajos académicos [5005]
Escuela Politécnica Superior de Gandia