JavaScript is disabled for your browser. Some features of this site may not work without it.
Buscar en RiuNet
Listar
Mi cuenta
Estadísticas
Ayuda RiuNet
Admin. UPV
Actuaciones para mejorar la eficiencia energética de una vivienda pluriifamiliar con una calificación baja en Catarroja
Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
Ficheros en el ítem
| dc.contributor.advisor | Navarro Calvo, Hector
|
es_ES |
| dc.contributor.author | Blanch Ramón, Salvador
|
es_ES |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2017-10-19T08:19:08Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2017-10-19T08:19:08Z | |
| dc.date.created | 2017-09-22 | |
| dc.date.issued | 2017-10-19 | es_ES |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10251/89518 | |
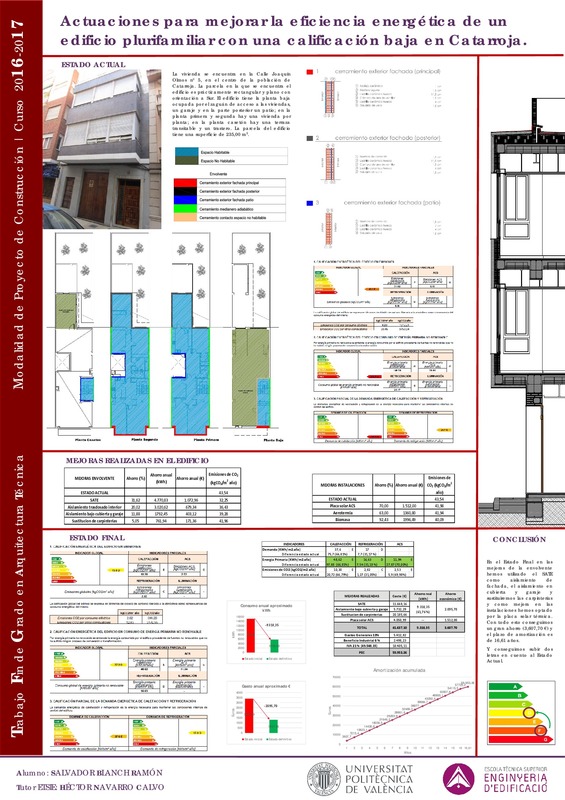
| dc.description.abstract | [EN] The architecture and all the parameters involved in the building design are the current response to the human needs of establishing the house with modified external environmental conditions to allow the development of different human activities in comfort conditions. The energy consumption of urban and building activity, together with the activities that support them, represents an important energy consumption of the urban environment. Part of that consumption is considered inevitable due to certain external environmental characteristics but can be reduced and optimized through different design strategies and the modification of energy habits of its occupants. In the last decades, due to the increase, the exhaustion and the impact generated on the biosphere by the use of fossil energy sources, appear a series of concepts whose objective is to recover the logic of the architecture adapted to the external environment. These are terms such as bioclimatic architecture, sustainable architecture, environmental architecture or bioarchitecture. They all have a common intention: to promote energy efficiency throughout the life cycle of the construction activity and reduce the impact on the habitat it generates. We have studied a building formed by two houses with low energy efficiency, and through the software program CE3x. A series of improvements will be analyzed in the envelope as well as in the installations, providing constructive solutions and efficient materials to obtain a higher rating. And an economic study and amortization of each solution and a comparison will be made to see which solutions are better from the energy point of view, taking into account the current regulations. But first we will talk about environmental impact and climate change, energy efficiency, sustainability, sustainable construction and bioclimatic. | es_ES |
| dc.description.abstract | [ES] La arquitectura y todos los parámetros que intervienen en el diseño edificatorio son la respuesta actual a las necesidades del ser humano de establecer a la vivienda con unas condiciones ambientales exteriores modificadas para permitir desarrollar las diferentes actividades humanas en condiciones de confort. El consumo energético que conlleva la actividad urbanística y edificatoria, junto con las actividades anexas que las sustentan, representa un importante consumo energético del medio urbano. Parte de ese consumo se considera inevitable en función de determinadas características ambientales exteriores pero que puede ser reducido y optimizado a través de diferentes estrategias de diseño y la modificación de hábitos energéticos de sus ocupantes. En las últimas décadas, debido al encarecimiento, el agotamiento y el impacto generado sobre la biosfera por la utilización de fuentes energéticas fósiles, aparecen una serie de conceptos cuyo objetivo es recuperar la lógica de la arquitectura adaptada al medio ambiente exterior. Son términos como arquitectura bioclimática, arquitectura sostenible, arquitectura medioambiental o bioarquitectura. Todos ellos tienen una intención común: fomentar la eficiencia energética a lo largo del ciclo de vida de la actividad constructiva y reducir el impacto sobre el medio que ésta genera. Con este trabajo se ha estudiado un edificio formado por dos viviendas con eficiencia energética baja, y mediante el programa informático CE3x. Se analizarán una serie de mejoras tanto en la envolvente como en las instalaciones, aportando soluciones constructivas y de materiales eficientes para obtener una calificación mayor. Y se realizará un estudio económico y amortización de cada solución y una comparativa para ver qué soluciones son mejores desde el punto de vista energético, teniendo en cuanta la normativa actual. Pero en primer lugar se hablará del impacto ambiental y cambio climático, la eficiencia energética, sostenibilidad, construcción sostenible y bioclimática. | es_ES |
| dc.format.extent | 216 | es_ES |
| dc.language | Español | es_ES |
| dc.publisher | Universitat Politècnica de València | es_ES |
| dc.rights | Reserva de todos los derechos | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Viviendas | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Eficiencia energética | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Auditoria energética | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Energy conservation | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Energy auditing | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Dwellings, Remodeling | es_ES |
| dc.subject.classification | CONSTRUCCIONES ARQUITECTONICAS | es_ES |
| dc.subject.other | Grado en Arquitectura Técnica-Grau en Arquitectura Tècnica | es_ES |
| dc.title | Actuaciones para mejorar la eficiencia energética de una vivienda pluriifamiliar con una calificación baja en Catarroja | es_ES |
| dc.type | Proyecto/Trabajo fin de carrera/grado | es_ES |
| dc.rights.accessRights | Abierto | es_ES |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Universitat Politècnica de València. Escuela Técnica Superior de Gestión en la Edificación - Escola Tècnica Superior de Gestió en l'Edificació | es_ES |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Universitat Politècnica de València. Departamento de Construcciones Arquitectónicas - Departament de Construccions Arquitectòniques | es_ES |
| dc.description.bibliographicCitation | Blanch Ramón, S. (2017). Actuaciones para mejorar la eficiencia energética de una vivienda pluriifamiliar con una calificación baja en Catarroja. http://hdl.handle.net/10251/89518 | es_ES |
| dc.description.accrualMethod | TFGM | es_ES |
| dc.relation.pasarela | TFGM\38272 | es_ES |
Este ítem aparece en la(s) siguiente(s) colección(ones)
-
ETSIE - Trabajos académicos [2383]
Escuela Técnica Superior de Ingenieria de Edificación