JavaScript is disabled for your browser. Some features of this site may not work without it.
Buscar en RiuNet
Listar
Mi cuenta
Estadísticas
Ayuda RiuNet
Admin. UPV
Estudio de la biodegrabilidad y grado de desintegración del films a base de almidón y PVA que incorporan diferentes sustancias antimicrobianas
Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
Ficheros en el ítem
| dc.contributor.advisor | González Martínez, María Consuelo
|
es_ES |
| dc.contributor.author | Peinado Devís, Marta
|
es_ES |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2015-10-22T18:10:28Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2015-10-22T18:10:28Z | |
| dc.date.created | 2015-09-09 | |
| dc.date.issued | 2015-10-22 | es_ES |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10251/56383 | |
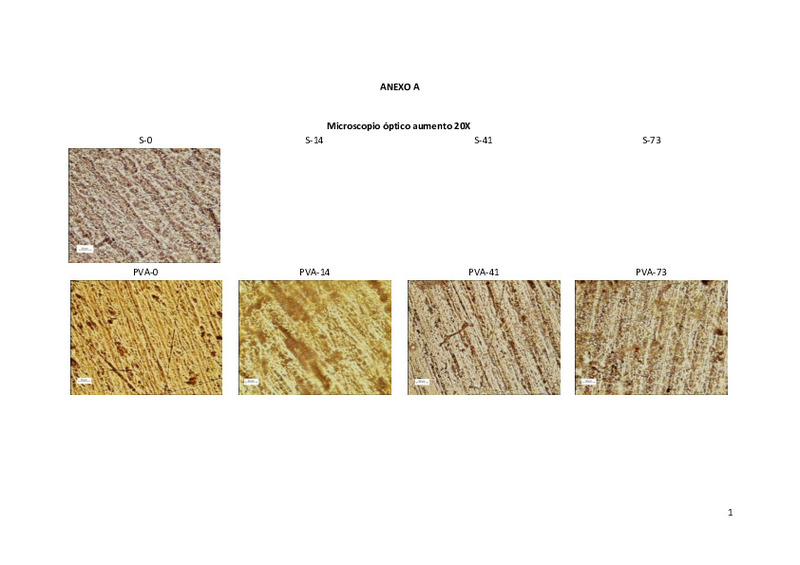
| dc.description.abstract | [ES] El presente trabajo tiene como objetivo evaluar la influencia de la incorporación de diferentes compuestos antimicrobianos en el proceso de desintegración y biodegradabilidad de envases a base de almidón de guisante y de polivinil alcohol. Las sustancias antimicrobianas fueron incorporadas a diferentes concentraciones de aceite de neem, aceite esencial de orégano y nanopartículas de plata. Para el análisis se llevaron a cabo dos ensayos. Un primer test de desintegración basado en la ISO 20200:2004 en el que las muestras estuvieron sometidas a condiciones de compostaje controladas durante 73 días. Además, se sacaron muestras del compost a cuatro tiempos diferentes (día 0, 14, 41 y 73) y se les realizó un estudio de su apariencia, microestructura y un análisis termogravimétrico con el fin de mejorar la comprensión de su degradación y ver la evolución que ésta sufre. El segundo ensayo basado en la ISO 14855-1:2012 fue un test de biodegradación, para el cual se registró periódicamente el CO2 emitido. Las películas puras mostraron comportamientos opuestos, presentando las películas de almidón el mayor porcentaje de degradación y biodegradabilidad y las de PVA el menor. Tanto las películas mezcla como las bioactivas mostraron un comportamiento intermedio entre las matrices puras presentando diferencias significativas (p ˂ 0,05) entre ellas. Por otra parte, los resultados muestran que la incorporación de agentes antimicrobianos no afectaron significativamente (p ˃ 0,05) a la desintegración y biodegradabilidad de las películas lo que es muy interesante para el desarrollo de envases que reduzcan la grave problemática medioambiental y alarguen la vida útil de los alimentos que contienen. Sin embargo, en el caso de las películas con nanopartÍculas de plata, los resultados mostraron una tendencia hacia un menor porcentaje de biodegradabilidad de las películas con la mayor concentración de plata debido a su acción sobre los microorganismos del compost. Por tanto, se recomienda utilizar concentraciones menores de plata para no comprometer el proceso de biodegradación de los mismos | es_ES |
| dc.description.abstract | [EN] The final degree work is focused on the development of new biodegradable packaging materials in order to reduce the generation of municipal waste. For it, pea starch, polyvinyl alcohol and starch-PVA blend films were developed. In addition, different antimicrobial compounds (neem oil, oregano essential oil and silver nanoparticles) at different concentrations were incorporated into the S-PVA film. The humidity and solubility of these films was determined. For the analysis of the films two tests were carried out. On the one hand, a disintegration test (ISO 20200: 2004) were assayed. Samples were subjected to controlled composting conditions for 73 days. Additionally, samples were removed from the compost at four different times (day 0, 14, 41 and 73) in order to evaluate their appearance, microstructure by optical microscopy, as well as to analyze by means of TGA. On the other hand, the second assay was a biodegradation test (ISO 14855-1: 2012) by means of the CO2 emitted. Both assays were validated. Pure films showed opposite behavior, whereas the starch films exhibited the highest percentage of disintegration and biodegradability, PVA provided the worst. The S-PVA blend and bioactive films showed an intermediate behavior between both pure films indicating significant difference (p ˂ 0.05). Moreover, no significant differences (p ˃ 0.05) in the percentage of biodegradation or disintegrability respect to S-PVA were found when natural antimicrobial agents were incorporated in the S-PVA matrix. This results are very interesting for packaging development to reduce the serious environmental problems and extend the food self- life. | es_ES |
| dc.language | Español | es_ES |
| dc.publisher | Universitat Politècnica de València | es_ES |
| dc.rights | Reconocimiento - No comercial - Sin obra derivada (by-nc-nd) | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Biodegradability | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Compostable | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Neem essential oil | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Oregane essential oil | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Silver nitrate | es_ES |
| dc.subject | ISO 14855-1 | es_ES |
| dc.subject | ISO 20200:2004 | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Biodegradabilidad compostable | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Norma ISO 14855-1 | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Norma ISO 20200:2004 | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Aceite esencial de neem | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Aceite esencial de oregano | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Nitrato de plata. | es_ES |
| dc.subject.classification | TECNOLOGIA DE ALIMENTOS | es_ES |
| dc.subject.other | Grado en Ciencia y Tecnología de los Alimentos-Grau en Ciència i Tecnologia dels Aliments | es_ES |
| dc.title | Estudio de la biodegrabilidad y grado de desintegración del films a base de almidón y PVA que incorporan diferentes sustancias antimicrobianas | es_ES |
| dc.type | Proyecto/Trabajo fin de carrera/grado | es_ES |
| dc.rights.accessRights | Abierto | es_ES |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Universitat Politècnica de València. Departamento de Tecnología de Alimentos - Departament de Tecnologia d'Aliments | es_ES |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Universitat Politècnica de València. Escuela Técnica Superior de Ingeniería Agronómica y del Medio Natural - Escola Tècnica Superior d'Enginyeria Agronòmica i del Medi Natural | es_ES |
| dc.description.bibliographicCitation | Peinado Devís, M. (2015). Estudio de la biodegrabilidad y grado de desintegración del films a base de almidón y PVA que incorporan diferentes sustancias antimicrobianas http://hdl.handle.net/10251/56383. | es_ES |
| dc.description.accrualMethod | TFGM | es_ES |
| dc.relation.pasarela | TFGM\29157 | es_ES |
Este ítem aparece en la(s) siguiente(s) colección(ones)
-
ETSIAMN - Trabajos académicos [3541]
Escuela Técnica Superior de Ingeniería Agronómica y del Medio Natural